13. Quiz Preparation - II
A. Overarching View
- Individual dimension of consumer behaviour
- Perception
- Decision Making
- Concept of self
- Social / collective dimension of consumer behaviour
- Social norms
- Household decision making
- Market behaviour: How do first organize our experience
- Consumer experience – Theme, Staging, and Actions
B. Decision Making
1. Individual dimension
- Involvement
- Perceived Risk
- Monetary Risk
- Performance Risk
- Physical Risk
- Social Risk
- Psychological Risk
- Decision Fatigue
- Utilitarian goods – Purchased for their practical and functional benefits
- Ego expressive goods – Purchased for their symbolic benefits; means of self-expression
Q. How does level of involvement influence consumer behavior? how should marketers take this into account?
- Topics: Involvement, Perceived risk, Cognitive dissonance
Cognitive dissonance
Also known as “consumer remorse” or “consumer guilt”, this is an unsettling feeling consumers may experience post-purchase if they feel their actions are not aligned with their needs.
A. Level of involvement is the degree of importance that a consumer attaches to a product or service. The higher the level of involvement, the more time and effort the consumer will expend in the decision-making process. Marketers should take this into account by providing more information to consumers with high involvement.
Q. Perceived risk and involvement related?
- Topics: Involvement, Perceived risk A. Higher the level of involvement, the higher the perceived risk.
2. Under low effort
- Sunk-cost Fallacy – tendency to justify increased investment in a decision, based on the cumulative prior investment
- Heuristics and Biases
- Heuristics: Mental shortcuts that help us make decisions quickly and efficiently
- Biases: Systematic errors in thinking that lead to irrational decisions
3. Family decision making
-
Family cycle (FLC)
-
Works as a unit (Syncretic decision making)
-
Different roles
- Initiator
- Gatekeeper
- Influencer
- Buyer
- User
-
Consensual Purchase Decision members agree on the desired purchase, they disagree only in terms of how they will make it happen.
-
Accommodative Purchase Decision group members have different preferences or priorities and can’t agree on a purchase that satisfies everyone’s needs.
-
Sex-role socialization – Children learn about the social expectations and attitudes associated with their own sex
-
Consumer socialization – Children acquire skills, knowledge, and attitudes that will help them function as consumers
C. Culture Influences
Culture: Set of lens which an individual views phenomena
- how individuals perceive and interpret phenomena, it provides the blueprint of human action.
- Cultural movement – culture is dyanmic and learned
Enculturation: Process of learning one’s own culture
Acculturation: Process of learning another culture’s beliefs and practices
Rituals: A set of sequential symbolic behaviors which is repeated periodically. These have enormous impact on brand loyalty and are effective ways to convey brand values.
- Brand rituals are invaluable for brands because they can increase the brand attractiveness.
Examples:
- Oreo’s “Twist, Lick, Dunk” ritual
- Placing a slice of lime in the corona bottle’s neck
| Rituals | Habit |
|---|---|
| Conscious and aware | Automatic |
| Symbolic | Practical |
| Meaningful practices with a sense of purpose | Practical practices |
Rites of Passage: A ritual that marks a transition from one stage of life to another
- Three dimensions of a rite of passage
- Separation – Leaving the old self behind
- Transition – Moving from one stage to another
- Incorporation – Becoming a new self
Examples:
- Birthdays
- Graduation
- Marriage
- Retirement
Myths: A story with symbolic elements that represent a culture’s idea and values
- Myths are powerful because they have an associated story and story-telling is a powerful way to communication
Other Definitions
- Norms
- Cultural capital – distinctive and socially rare tastes and practices
- Brand community
- Brand fests
- Habitus – socially-ingrained habits, skills, and dispositions
- Two step flow of communication
- Information flows from the mass media to opinion leaders
- Opinion leaders then communicate it to the general public
D. Consumer Experience
Different phases of consumer experience
- Pre-consumption experience
- Purchase experience
- Core Consumption experience
- Remebered consumption experience
Peak-end rule: The tendency for consumers to remember the peak and end of an experience, rather than the middle.
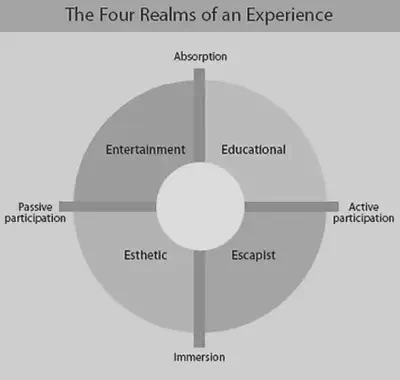
- Active - Customers actively influence the performance, thereby creating a unique experience
- Passive - Customers purely observes or listens
Experiential context framework
A mix of stimuli such as as the decor or activites that are designed to generate a specific consumption experience.
- Stage – The environment in which the experience takes place
- Costumes
- Design of the stage
- Music
- Theme – The story being told by the experience
- Actions - Activites that the consumer performs or experiences
F. Social Dimension of Consumption
- Social Norms – implicit codes of conduct that provide a guide to appropriate action in a given situation.
| Descriptive Norms | Injunctive Norms |
|---|---|
| What other people do in a social circle | What people should do; Behaviours that one is expected to follow and expects others to follow in a given social situation; |
According to “The forms of capital”, there are three types of capital:
- Economic capital
- Social capital - the collection of social relations one has at one’s disposal
- Cultural capital
Cultural Capital
Forms of knowledge, skills and education, as well as socially rare tastes and practices that a person has, which give them a higher status in society.
G. Concept of self
- Self-concept, self-esteem, extended self
- self-congruence theory
- Looking glass self
- Actual vs Idea self
- Social comparison theory: Humans have a drive to evaluate themselves and that they evaluate themselves by comparison with others
- Dramaturgical perspective: The metaphor of life as theatre and people as actors who play different roles
- Impression management
H. Perception
- Mere exposure effect – the tendency for liking to increase with the frequency of exposure
- Perception process – process by which stimuli are selected, organized and interpreted
- Cross-modal perception – perceiving/intneracting with something in two or more different senses
- Exposure
- Absolute threshold – the minimum amount of stimulation that can be detected
- Difference threshold – the minimum amount of change in stimulation that can be detected
- Weber’s law – the principle that the difference threshold is a constant proportion of the intensity of the stimulus
Furthermore, there are different types of tendencies that affect perception:
- Perceptual vigilance
- Perceptual defense
- Schemas – set of belief about objects, ideas or people
Other important concepts:
- Contrast
- Perceptual Maps
I. Interviews vs Surveys
| Interviews | Surveys |
|---|---|
| Interview is a formal conversation between the interviewer and respondent | Survey is a questionnaire that is filled by the respondent |
| The questions are open-ended | The questions are closed-ended |
| Sample size is small | Sample size is large |
| Structured and improvised at the same time | Completely structured beforehand |
| Subjective in nature | Objective in nature |
| Time consuming | Time efficient |
| Expensive | Cheap |
1. Designing an interview guide
- Define the key areas – Mind map
- Building the opening
- Funnel the questions
- Facts
- Behaviour
- Opinions/Feelings
- Add questions to elicit more information
- Review
Example:
- WARM-UP
- Life situation, families, kids etc.
- What’s going on in life
Projective techniques – indirect questioning, enables the respondent beliefs and feelings onto third party Examples:
- Sentence completion
- Third person test
- Obituary
APX. Essay Answer Structure
- Identify the key concepts that can be used to explain the question
- Explain the key concepts
- Apply the key concepts to the question
- Avoid long sentences
- Use bullet points (if appropriate)
- Provide examples
- Draw conclusions