1. Computer fundamentals
1. Endianness
The order or sequence in which the bytes of a data is stored in a computer memory. It is expressed as big-endian (BE) or little-endian (LE).
Big-endian: The most significant byte (MSB) is stored at the smallest memory address.Little-endian: The least significant byte (LSB) is stored at the smallest memory address.
2. Stack & Heap: Memory Allocation and management in python
When a variable is declared, for example x=10 and x=y both have the same value memory, i.e both variable points to the same object. Python optimizes memory utilisation by allocating the same object reference to a new variable if object already exists in memory with same value.
Memory address stored by a variable can be found using id().
The order of memory allocation in RAM is as follows (Low to high),
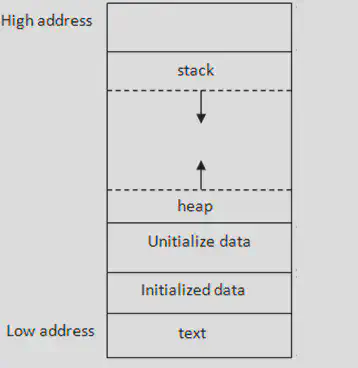
Heap is responsible to store all the values. A stack stores hold the references to the objects in the heap.
The name heap and stack does not have any relation to the data structure.
3. Processes and Threads
A process is a program that is currently under execution, whereas a thread is an execution entity that reside within a process that can be scheduled for execution. 1
A thread is an execution unit with its own stack and set of registers that reside in a process. A thread always belongs to exactly one process.
Threads are also known as light-weight processes.
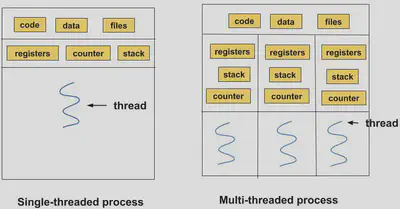
In a multi-threaded process, each thread has its own stack and registers but shares the same memory. This lets access to code segments, files and data be shared among threads.